Electro mechanical systems laboratory
[Japanese]
 Professor
Junji HIRAI
Professor
Junji HIRAI
hirai@elec.mie-u.ac.jp
Associate Prof.
Satoshi KOMADA
komada@elec.mie-u.ac.jp
Associate Prof.
Kazuhiro YUBAI
yubai@elec.mie-u.ac.jp
Tech. Staff
Masaru NAKAMURA
nakamura@elec.mie-u.ac.jp
Electro mechanical systems laboratory Home Page
With the recent great progress of electronics techniques, research activities
in "Electrical powerengineering laboratories"
at universities have focused on the conversion and control
of electric power using electronics techniques,
in the names of "power electronics", "motion control" and "
mechatronics ( robotics in particular ) "
In the line of such a research trend, our laboratory is extending its R&D
activities further to intelligent motion control,
next-generation robots servingor co-existing in the human society,
and the system composed of such intelligent robots.
Up to present, robots have been widely used for industrial purpose especially
in the production lines. From now on, however, they are getting into human
society as welfare, nursery or amusement partners. In circumstance of such
co-existing or coordinated life between human beings and robots, the robots
have to make a right decision and execute an appropriate action on the
basis of external sensor information on position, force and visual image.
In order to perform so autonomously, the robots themselves must be provided
with such sophisticated intelligence and judging function as the human
beings inherently have. For cooperative work with the human beings, the
robot control requires soft-touch motion controllability more than precise
and rigid motion controllability. How to perform the human-like motion
is prioritized first for human partner robots, accordingly. Moreover, with
the progress of such cooperative society, the conventional centralized
robot control inevitably comes to be impossible. Hence, the autonomous
robot is sought for which can detect and deal with accidents by itself.
Thus, the motion control research on the robots co-exiting and cooperating
with the human beings involves various items which seem much interesting
but have been left undeveloped so far.
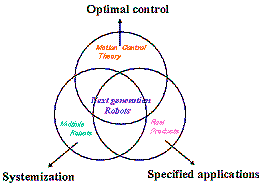
On the standpoint mentioned above, R&D activities are being carried
out in our laboratory for the items categorized in the three major directions
from the core target "creation of next generation robot", as
shown above:
The latest research topics at our laboratory includes:
1. Survey on optimal motion control
Realizing fast and precise motion control which is a basic requirement on dexterous robot
manipulation is aimed at. In practical situations, non-linearities and modeling errors cause
serious performance degradation.
In order to avoid performance degradation under some
system uncertainties, studies on disturbance observer and robust control are being carried out.
2. Research on robotic intelligence and systemization of group robots
In pursuit of the next-generation robots which can perform their motion autonomously like
human beings, R&D works are being done on a robot which makes a motion strategy and
performs it on the basis of visual information from cameras.
Besides, in order to realize the dexterous and flexible motion of human beings,
motion strategy of human beings is analyzed and applied to robot manipulation.
Moreover, in order to achieve some objectives
through plural-robot cooperation, a research on cooperative motion among multiple robots is
being performed.
3. Application-specified next-generation robots
Through introduction of novel control theory and innovative actuators, R&D activities are
being carried out so as to realize the next-generation robots which can co-vive with human
beings or surpass the human function and performance in particular aspects. Our laboratory
aims at conceptualizing and embodying a revolutionally novel robot, for example an easily
re-configurable modular robot utilizing the non-contact motion transfer as well as the
state-of-the-art human-skill based theory like impedance control or fuzzy-based decision making.
The object to be manipulated by such next generation robots includes not only conventional
metallic and/or rigid materials but also the human bodies or bio-materials like living cells
which can not be handled without soft-touch manipulation by means of sophisticated motion control.
www-admin@elec.mie-u.ac.jp
 Professor
Junji HIRAI
Professor
Junji HIRAI